The video streaming industry has solidified itself as an economic driver globally, with projections indicating that by 2032 it will grow to $2,660 billion in value.
This anticipated growth is fueled not only by an increasing global demand for digital streaming services but also through technology advancements, delivery innovations, and better security initiatives that protect both content providers and consumers. Perhaps one of the biggest security initiatives across the industry involves the crackdown on password sharing.
After Netflix and Hulu were estimated to have previously lost billions a year from password sharing, the industry has collectively taken notice. Increased competition, lost potential for revenue optimization, partnership obligations, shareholder pressure and ever-changing piracy tactics have contributed to an environment where multiple streaming services are now cracking down on password sharing, among them Netflix, Disney, Hulu and Max—with more certainly to follow.
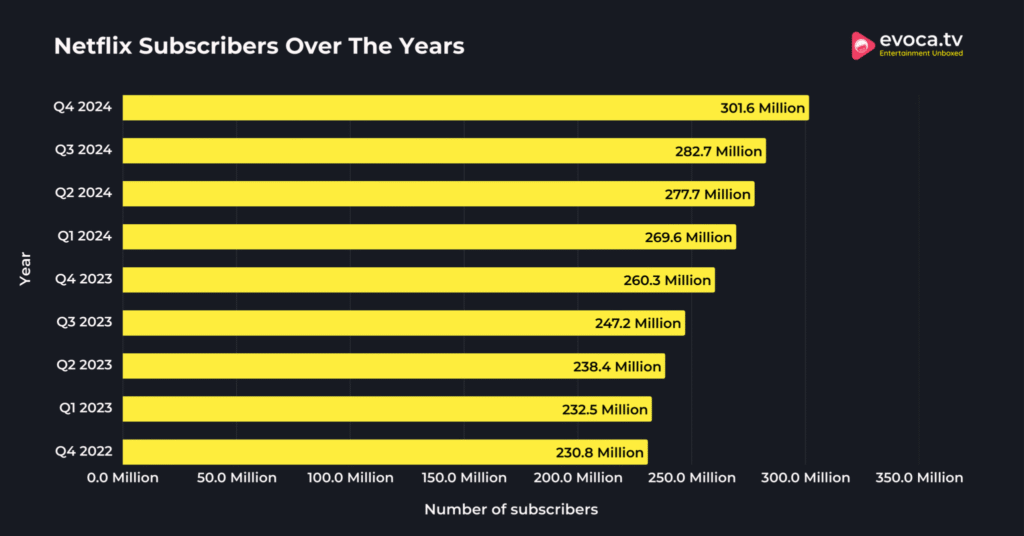
Since alerting subscribers in the United States that it would begin to curb password sharing on May 23, 2023, Netflix has had the four single largest days of U.S. user acquisition. Based on the most current data available, Netflix saw nearly 100,000 daily sign-ups on both May 26 and May 27—with healthy quarterly global subscriber additions continuing through 2024.
But while the first phase of password-sharing crackdowns is having an impact, there is still work to be done. According to recent surveys, upward of 79 percent of Americans admit to sharing passwords on streaming accounts with someone outside their homes.
As streaming retail prices continue to rise, consumers will continue to look for ways to circumvent the subscription system to get entertainment for free or at a price that is lower than what it should be. Surprisingly, a significant number of streaming services are not following the lead of industry giants due to one or a combination of these factors:
- Platform or delivery technical limitations
- Backlash from subscribers
- Fear of disrupting the overall user experience
- Competitive pressure to offer content anywhere, at anytime
- Internal resistance from leadership or tech teams
- Accuracy of data to allow/restrict access based on geography
Fortunately, a comprehensive data-driven solution built on IP address intelligence gives streaming service providers the ability to more reliably identify password violations and capture revenue without losing subscribers.
IP Intelligence Data as the Solution
IP intelligence is a collection of data and technologies related to IP addresses that can be used to understand online user behavior and identify threats in a more privacy-sensitive manner.
IP intelligence delivers not only the geographic location of the IP address, but also IP characteristics including the connection type, ISP, domain details, organizational data, location stability, number of devices observed for a given IP address, and insights into anonymized connections specific to VPNs and proxies.
It’s important to note that not all IP intelligence data providers are created equal. IP addresses can be re-allocated at the discretion of internet service providers (ISPs), and frequently are.
Reliable IP intelligence data, therefore, requires network geography experts to regularly apply their experience and judgment in order to resolve ambiguities. It must also be constantly updated using the most current data from multiple sources.
Beyond being reliable and up-to-date, the most important qualities to consider when evaluating IP intelligence data providers include:
- Granularity: The more precisely you can determine a location, the better you can detect password sharing. A single account with logins from different continents is easy to flag, but sharing is just as likely to occur between friends in the same city. Ideally, geolocation attributes will include not only country and state, but also city, DMA, and postal or ZIP code.Support for IPv6 as well as IPv4: While most addresses still use the older v4 Internet Protocol, use of IPv6 is growing, particularly for mobile devices. You’ll get an incomplete picture without data from both protocols, and it will only get worse in the future.
- Ability to detect logins from anonymous proxy servers and VPNs: Proxy and VPN usage masks a user’s actual IP address and allows them to log in anonymously. In fact, studies indicate that the residential proxy server market is projected to grow substantially in the coming years, which adds yet another threat. Residential proxies are another method to cloak online users’ identities, as these types of proxy networks channel internet traffic through real-world IP addresses provided by ISPs. All this may be completely innocent, or a deliberate attempt to utilize someone else’s password. Either way, knowing what percentage of traffic is affected by this technology is the first step in understanding how big (or small) the challenge is.
- Compliance with consumer privacy regulations and standards: To avoid the possibility of heavy fines and negative publicity, IP intelligence data must comply with privacy regulations such as Europe’s GDPR and California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and must not comprise personally identifiable information (PII).
- Flexible delivery methods: In this day and age, companies don’t need long, drawn-out technology and data integrations. The ability to deploy IP intelligence solutions to support how your team works—whether it’s API-based server software, flat-file downloads or a high-performance cloud service—means a quicker, more seamless integration with your IT systems or platforms.
- Data beyond geolocation: IP Intelligence begins with reliably pinpointing an IP address’ location. It is imperative to have sophisticated processes to provide geolocation data down to a postcode level, laying the foundation for deeper insights into the identity and behavior behind an IP address. See IP characteristics above. Some providers also offer risk insight data that flags suspicious IP addresses and non-human (bot or server) traffic. This kind of intelligence can help identify more serious password threats, such as dictionary attacks, in addition to individual password sharing. It also ensures that geolocation-based initiatives to prevent password sharing are focused on actual humans.
- Support and service: Dedicated 24/7 support teams staffed with seasoned industry experts can help you leverage IP intelligence data to create the most value for your streaming business—based on your needs and circumstances. These specialists will also be able to collect and decipher risks, identify the red flags deserving of a customer prompt, and know when to follow up with further action.
How Streaming Media Companies Are Leveraging IP Intelligence Insights
Here are some real-world use cases from streaming media companies that are successfully utilizing IP intelligence insights to curb password sharing:
Identifying login locations
The simplest and surest way to identify password sharing is to pinpoint accounts with regular logins from multiple, geographically separate locations.
IP geolocation data, which associates a user’s IP address with geographic location information: where they are logging in, how they are connecting to the internet, and more. IP geolocation decisioning data helps you set your organization’s rules for allowing access and establishing criteria for suspicious behavior—so the more granular this data is, the better.
To enforce password-sharing guidelines, you’ll want to use the most robust and current IP geolocation data available. This ensures you can accurately locate your users and identify logins originating from alternative locations, which may indicate password compromise.
Managing anonymous users
Increasingly more online users are consuming content through a VPN or proxy server. This masks their originating/assigned IP address and allows these users to log in anonymously. Not all proxy use is nefarious.
However, when someone uses a proxy server to mask their location for the purpose of evading geographic boundaries, their action may violate terms of service or content viewing restrictions. In some cases, the action may be prohibited.
Location masking complicates the determination of password sharing. If you can’t assess the location from which your users are logging in, it makes it difficult to identify fraudulent logins from alternative locations.
IP intelligence data lets media providers create rules to both “geo-authenticate” users and “geo-fence” their content if necessary. This blocks unauthorized users from connecting from outside of an approved area.
Creating user profiles
Providers can incorporate IP intelligence information for logins to develop user data sets. The data structure accommodates a time-stamped record of every login for each subscriber, as well as the type of connection, including VPN and proxy servers. This record enables the creation of a baseline geo-footprint of normal logins for each user.
The baseline for most users will be a single location, or two nearby locations—representing a home and an office, for example. Some users, however, may travel extensively and regularly, logging in from Boston one day, Houston the next, and São Paulo the following week. The file structure must be flexible enough to accommodate the profiles of these frequent travelers.
Any departure from a baseline pattern could indicate password sharing for an account— but it could also just be the result of travel. To more accurately identify actual password sharing, providers can take these additional factors into account:
- Velocity checking for logins from multiple locations: A login from a new location eight hours after a baseline location could be the result of legitimate travel; a login that occurs five minutes later from a different state or country is probably not.
- Change in type of connection: When a customer who regularly connects via a conventional ISP logs in via a proxy server, it may indicate password sharing.
- Logins from suspicious IP addresses: Even a first-time login from an IP address that is associated with risky activity is cause for concern.
Executing a “soft” enforcement approach
Since the goal is to limit password sharing while retaining legitimate customers, providers should act on the insights they obtain with the presumption that customers are innocent. No one wants to be accused of wrongdoing, or blocked from seeing a much-anticipated movie, program or sports event. Conversely, customers are generally supportive of efforts to protect the security of their accounts.
Providers are adopting a “soft enforcement” approach that reaches out to flagged users with friendly messages that engage them and ask for their help, rather than scold or accuse them. Your initial communication might include:
- Messaging that assumes legitimate behavior and indicates concern: “We saw you logged in from a new location, and want to ensure that your account has not been compromised.”
- A request for verification and a convenient way to provide it: “Please confirm your user ID and password at this link, or by calling our confirmation hotline toll-free at 1-800-XXX-XXXX.”
A comprehensive outreach program will include calibrated escalations for unanswered requests, while continuing to assume innocent behavior. For example, a second message might start by noting that “we haven’t heard from you regarding a new login location,” and request a response by a specific day to “ensure the safety and security of your account.”
Continued non-response might result in a notification that the account will be blocked unless the customer verifies his or her identity to ensure account security. Only a failure to respond to this third request would result in a block on the account, accompanied by a message that “your account has been blocked to ensure your security” and inviting the customer to get in touch to provide verification.
Rely on a Smart Strategy to Fight Password Sharing
Although the login for an NFL Sunday Ticket package may be shared across a Fantasy Football League or a Netflix password might find its way from a roommate to a classmate to a boyfriend’s cousin, content providers now have a smarter strategy to fight password sharing.
With the right IP intelligence data, streaming media providers can strengthen their ability to identify suspicious activity and configure effective access criteria and rules—enabling them to capture revenues, retain subscribers, encourage account upgrades, and increase customer satisfaction.
Are you ready to implement a smart strategy to fight password sharing? Reach out to support@digitalenvoy.com today!